UVM's completed STEM (science, technology, engineering, mathematics) complex made its campus debut in 2019 as a state-of-the-art facility housing laboratories, classrooms, and research facilities to best prepare our students with hands-on opportunities for learning and research. As a CEMS student, most of your classes will take place here, in some of the most advanced learning spaces in the state, helping you develop your academic interests and preparing you for a promising career.

Features
The STEM complex at UVM sits at the center of campus and includes:
- Three interconnected buildings housing the engineering, mathematics and statistics, physics, and computer science departments.
- Twenty state-of-the-art teaching labs
- Seven media-rich classrooms that foster team-based learning and engaging, problem-based teaching
- Faculty labs that promote innovation and collaboration
- Comfortable meeting spaces for student and faculty interaction
Some of our State-of-the-Art Labs
Fabrication Lab (FABLAB)
An incubator for ideas and a place to engage people’s imaginations, the UVM FabLab makes rapid-prototyping tools available to UVM students and faculty. The lab provides the opportunity for interaction in developing and testing innovative products and designs. We encourage projects that support research, innovation, and creativity, and student work that is supported by coursework and professors. Located in Votey 242, the FabLab houses an expanding collection of the latest rapid-prototyping tools that are readily available to the CEMS community.
Prototype Lab
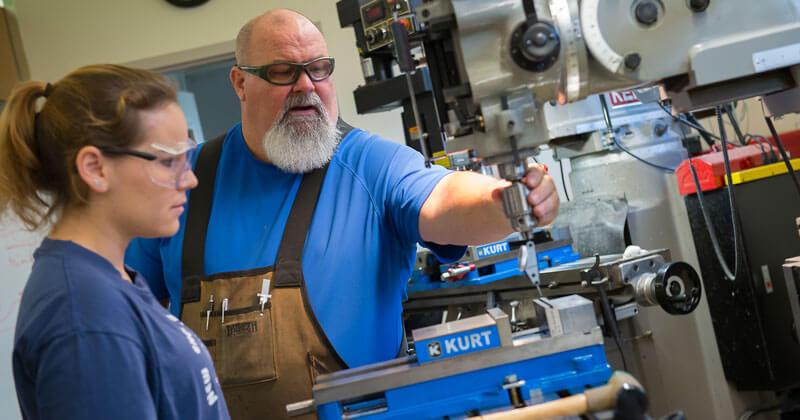

Located in Votey 125, the Prototype Lab (aka The Machine Shop) is a resource for students and faculty needing assistance with prototyping, specifically metals machining. The shop houses two HURCO CNC's, OMAX Waterjet, mills, lathes, horizontal and vertical band saws, and a welding area. The shop is used by ME081 Mechanical Engineering Shop Experience students and is a resource for student projects and research labs.
Device Characterization Teaching Lab
The groundbreaking Device Characterization Teaching Lab was created through a unique and mutually advantageous collaboration between the University's College of Engineering and Mathematical Sciences (CEMS) and GlobalFoundries. The new lab features a suite of scientific testing and analysis equipment donated by GF and heralds an essential phase of the ongoing initiative to prepare students to work in the rapidly expanding field of semiconductors.
Learn more about our Semiconductor Engineering and Physics
Mechanical Engineering/Civil & Environmental Engineering Labs
Fluids Laboratory

Votey 101
1600 Sq ft.
Laboratory Supervisors: Will Louisos and George Pinder
Courses that use the laboratory:
• CE 162 – Hydraulics Lab
• ME 123 – Thermo-Fluid Lab
• CE 265 – Ground Water Hydrology
Major Equipment:
- 6-meter Re-circulating Flume and acrylic weirs: Engineering Laboratory Design, Inc. Purpose: The flume is used to create hydraulic jumps, analyze energy losses through the jump, and compare measured and theoretical depths downstream of the jump. Weirs are used in combination with a point gage to measure the pressure head and flow rate under different channel conditions.
- Hydraulics Benches Armfield F1-10B: Used in conjunction with Venturi meters, sharp edge orifices, centrifugal pumps, and Osbourne-Reynolds demonstrations. The smaller bench format allows students to gain hands-on experience in small groups.
- Venturi meter, pressure taps, and mercury manometers Armfield F1-15: Used to demonstrate Bernoulli’s Theorem. Students used the Venturi meter to determine flow characteristics through a pipeline meter, associated discharge coefficients, and measure the head losses in a pipeline meter.
- Sharp-Edged Oriface and Free Flow Jet Armfield F1-17: Used to determine the characteristics of flow through a small-edged orifice and to determine the coefficients of contraction, velocity and discharge.
- Centrifugal pumps Armfield F1-27-G: Used to determine the constant speed characteristics of a centrifugal (radial flow) pump. Characteristics include head-discharge, power-discharge, and efficiency-discharge. The motor is instrumented with a Watt meter for power consumption readings. Bourdon-type pressure gages indicate the suction and discharge pressures, and discharge is measure by gravimetric methods.
- Dead Weight Calibrator Armfield F1-11: Used to calibrate the Bourdon-type pressure gages.
- Osbourne-Reynolds Apparatus Armfield F1-20: Used to study laminar flow, transitional flow, turbulent flow and associated velocity profiles. Velocity measurements are used to calculate Reynolds numbers.
- Hydrometers Custom built: Clear, acrylic, cylindrical tank with seat hole in the bottom and small side drain. Used to study the relationship of hydrostatics as it relates to forces on submersed bodies.
- Water meter and test stand: Used to study the characteristics of a household water meter and determine its usefulness as a flow measuring device.
- Flotek 1440 Wind Tunnel: Used to study the properties of air flow around various objects including air foils.
Clean Materials Laboratory
Votey 246
600 sq. ft
Laboratory supervisor: John Novotny
Courses that use the laboratory:
- ME124 – Materials and Mechanics Laboratory
Major equipment:
- Dynamic Fatigue Testing Station (1) Instron 8801, Instron, Inc. Purpose: Perform fracture mechanics testing on steel specimens, including dynamic loading of dogbone specimens. Currently used with the Epsilon 3542 Axial Extensometer.
Materials & Structures Laboratory
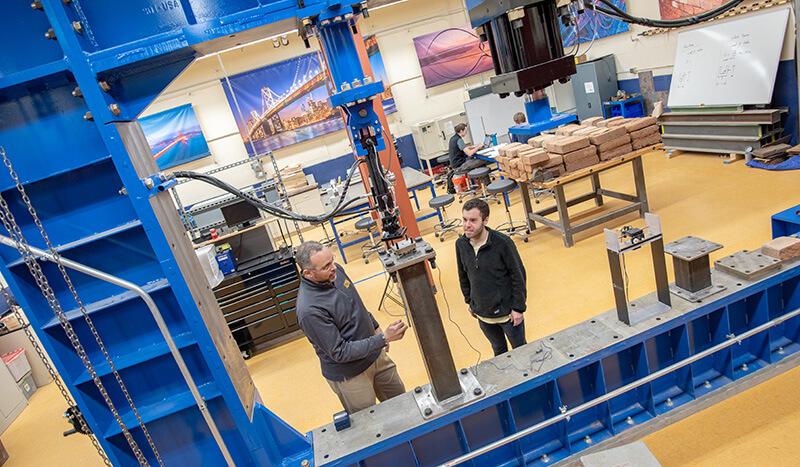

Votey 114A
1545 sq. ft
Laboratory supervisor: Priyantha Wijesinghe
Courses that use the laboratory:
Major Equipment:
- COMING SOON! Dual Actuated Reaction Frame with 2" cylinder (3 kip) and 10" cylinder (150 kip) and RMC70 series Delta motion control for dynamic compression and tensile testing. DARF testing control is located in the Votey 114 Observation Room.
- Tinius Olsen Loading Apparatus – Capacity 60,000 lbs. with screw gear drive and MTS control. The Tinius was a military donation at the time that Votey Hall was constructed in 1964 and has been in use over since. The Tinius is used in the Mechanics of Materials course to test standard specimens of various metals (steel, aluminum, brass, copper, cast iron. etc.) and for testing wood beams, small concrete beams, and student designed balsa wood trusses. It has been used for industrial purposes such initial testing by Burton Snow Boards and numerous other items of interest to local industries.
- Concrete Compression Testing Machine – Capacity 300,000 lbs. Humbolt HCM-2500. Used to compress student-made concrete cylinders and cylinders collected in the field.
- Dynamic Analysis Equipment available with accelerometers and impact hammers.Used to test the vibrations of small and large scale models.
- Surveying equipment – TopCon laser levels, optical and laser tribrachs, GPS systems, prism poles, level rods and tripods. Used in the CE 010 Geomatics course.
Geotechnical Laboratory
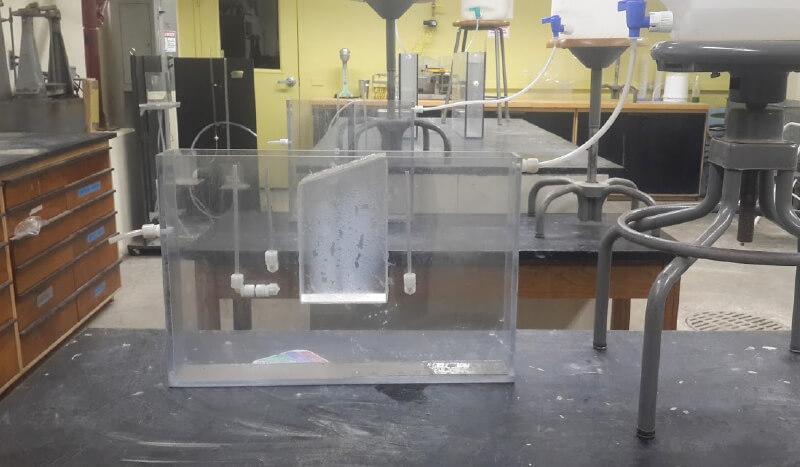
Votey 127
1400 sq. ft
Laboratory Supervisor: Mandar Dewoolkar
Courses that use the laboratory:
CE 182 – Geotechnical Principles Lab
CE 281 – Geotechnical Design
CE 185 / CE186 – Capstone Design I & II
Major equipment:
- Fully Automated Direct Shear Device (1). Purpose: To study shear strength of soils. The apparatus can also be used to perform reversal direct shear tests.
- Fully Automated Combined Consolidation and Triaxial Device (1). Purpose: To study compressibility and shear strength of soils (drained, undrained, mixed, isotropic or anisotropic testing)
- Instructional Centrifuge with Digital Image Analysis (1). Purpose: To study stability problems (slope stability, retaining structures, and shallow foundations).
- Constant and Falling Head Permeameters (5). Purpose: To study hydraulic conductivity of soils.
- Standard and Modified Proctor Devices (5). Purpose: To study compaction behavior of soils (includes proctor molds, hammers, and one automated hammering device).
- Casagrande Devices for Atterberg Limits (5). Purpose: To study consistency limits (liquid limit and plastic limit) of soils.
- Fall Cones (2). Purpose: To study consistency limits (liquid limit and plastic limit) of soils.
- Sieve Sets and Hydrometers (5). Purpose: To study grain size distribution of soils.
- Sand Cone Apparatus (5). Purpose: To study in situ density of soils.
- 2-D Acrylic Seepage Models (3). Purpose: Used to observe seepage behavior in the subsurface. Students use these models to determine the parameters of elevation, pressure, and total heads, flow rate, and hydraulic conductivity.
- Hand Operated Field Equipment including Augers, Shelby tubes, and samplers (2). Purpose: To auger and retrieve soil samples from subsurface.
Environmental Engineering Laboratory
Discovery W218
633 sq. ft
Laboratory Supervisor: Britt Holmen
Courses that use this laboratory:
- CE 254 – Environmental Quantitative Analysis
- CE 003 – Introduction to Civil & Environmental Engineering
Major Equipment:
- Water quality analysis
- Dissolved Oxygen Meters (6)
- pH Meters (6)
- Conductivity Meters (3)
- Turbidity meters (6)
- Hand-held Multimeters (6)
- Microscopes (6), Standard Optical
- Spectrophotometers (2)
- Drying oven (1)
- Incubator (1)
- Benchtop centrifuge (1)
- Peristaltic pumps (3)
- Constantly flowing stirred tank reactor model (2)
- Plug flow reactor model (1)
- GC-FID (1), Gas chromatography with Free Induction Decay detection
Shared UVM Facilities
Animal Care Management
Supports biomedical, biological, and behavioral research with a commitment to using animals ethically and compassionately. The University veterinarian provides oversight and clinical care for animals utilized in University teaching and research activities.
Biostatistics
Supports research study design, statistical analysis, and reporting results.
Flow Cytometry and Cell Sorting
Multi-user resource for the high speed analysis and sorting of cells.
Genomic Medicine Laboratory
The Genomic Medicine laboratory is accredited by the College of American Pathologists and certified as compliant with Clinical Laboratory Improvement Amendments.
Instrumentation and Model Facility
Provides functional prototypes, custom instruments, integrated systems, precision parts, and accurate models.
Mass Spectrometry
Provides proteomic analyses focused on quantification of proteins and posttranslational modifications, small molecule quantification, metabolite pattern identification, and measurement of rates and kinetics.
Microscopy Imaging Center
Multi-user resource for sample preparation and collection and analysis of images for biological and materials applications.
MRI Center For Biomedical Imaging
Specializes in functional MRI (fMRI) and neuro imaging and imaging of almost any anatomical structure via state-of-the-art 3T MRI scanner.
Proteomics Facility
Provides a central resource of mass spectrometry-based proteomics technologies to identify, characterize, and quantify target proteins in various biological and biomedical samples.
Vermont Advanced Computing Center
Provides rapid access to large-scale advanced computing infrastructure while offering responsive technical support.
Vermont Integrative Genomics Resource
Offers DNA/RNA analysis services, microarray global gene expression profiling, genome-scale next-generation DNA sequencing at the Massively Parallel Sequencing Facility, and bioinformatics genomic sequencing, epigenetic modification, or expression services.